With the continuous development of mobile communication technologies, the Internet of Things such as low-power wide area network (LPWAN) has ushered in rapid development.
From the comparison of NB-IoT and eMTC technologies, look at the selection strategies of China's three major operators on NB-IoT and eMTC.
From the perspective of global operators, AT&T, Verizon, KDDI, KPN, Orange, NTT DoCoMo, Telefonica, Telstra, Telus, etc. have all started commercial use of eMTC.
In China, China Telecom took the lead in the race. After establishing the 800MHz networking capability, it plans to build 300,000 NB-IoT base stations; China Unicom and Jasper signed a double-exclusive agreement, and early identified NB-IoT as the development direction; China Mobile, which is connected to the Internet, is uncertain between NB-IoT and eMTC. The main reason for this is that the two systems have their own strengths, and China Mobile's TDD network also determines the entanglement in its decision-making.
This paper will attempt to analyze the promotion strategies of China's three major operators on NB-IoT and eMTC from the perspectives of demand, technology and status quo.
The current caliber of the first and third operators
First look at China Unicom, China Unicom recently announced that it will deploy eMTC network in time in 2018; Chairman Wang Xiaochu also introduced at last week's shareholders meeting: "In the long run, we are more concerned about eMTC. Because of the need for high traffic, low latency. Application scenarios such as car networking must be a combination of 5G+eMTC. From the above perspective, China Unicom has played a Taiji, but there is no clear eMTC development plan.
Looking at China Telecom, China Telecom basically does not mention eMTC. It is reported that its official calibre is "according to standards, industry maturity, and timely introduction." Obviously, China Telecom does not have a clear eMTC development plan, and it is a sidewalk.
Finally, looking at China Mobile, China Mobile did not publicly announce its eMTC plan, but in terms of actual progress, it is the eMTC investment of the three major operators. Currently, it has deployed and verified eMTC networks in multiple cities. . The author speculates that because TDD licenses and NB-IoT do not support TDD for the time being, on the one hand, China Mobile has repeatedly claimed that it will focus on NB-IoT technology, pressure government organizations to promote the acquisition of FDD licenses; I am sure that I will be able to obtain an FDD license, which may not be available at least in the short term. Therefore, China Mobile has adopted a strategy of footing two boats to develop NB-IoT and to comply with eMTC technology.
Second, NB-IoT and eMTC technology comparison
Both are low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies, and the two have technical advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of NB-IoT are lower cost, wider coverage, and larger cell capacity. The main advantages of eMTC are higher speed, better mobility, and support for voice. The detailed comparison between the two is as follows:
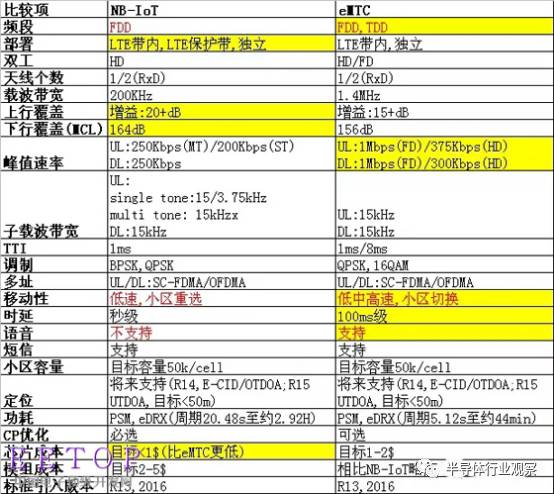
It is easy to see that both NB-IoT and eMTC are narrowband LTE technologies, which means they can utilize existing infrastructure and spectrum, but NB-IoT and eMTC are both at the transmission rate compared to existing LTE networks. Greatly reduced.
NB-IoT uses a bandwidth of approximately 200KHz and supports low-traffic data at rates below 100Kbps. The eMTC technology uses 1.4MHz bandwidth with a maximum data transfer rate of 1Mbps.
This also further reduces the complexity of the terminal and core network, enabling lower power consumption and longer battery life, and deeper coverage through redundant transmission. It is fully in line with the current requirements of IoT devices for low transmission rate, low power consumption and low cost.
NB-IoT technology has the following advantages:
(1) Strong connection: The wall penetration capability increases the gain by 20dB over Cat.4 LTE. In the case of the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50-100 times more access than the existing wireless technology. One sector can support 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption, and optimized network architecture;
(2) Ultra-low power consumption: Since NB-IoT focuses on small data volume and low-rate applications, the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, and the battery life can be greatly improved from the past few months to several years. More than ten years;
(3) Deep coverage: It can achieve 20db higher coverage than GSM, which is equivalent to 100 times coverage area; (4) Low cost: NB-IoT is built on cellular network and can be deployed directly on GSM network, UMTS network or LTE network to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrade; at the same time, low speed, low power consumption and low bandwidth also bring low cost advantages to NB-IoT chips and modules. (
5) Security: Inherit 4G network security capabilities, support two-way authentication and strict air interface encryption to ensure the security of user data;
(6) Stable and reliable: It can provide carrier-class reliability access and effectively support IoT applications and smart city solutions.
Compared with NB-IoT technology, eMTC also has many of the above features, but it is different from NB-IoT in signal coverage depth (through-wall capability is 15dB higher than Cat.4 LTE), power consumption and cost. However, the advantage of eMTC is that the transmission rate is faster, lower latency (100ms level, NB-IoT is second level), support mobility, FDD, positioning, support VoLTE voice communication. However, when the NB-IoT of the 3GPP Release 14 standard comes out, it can also support features such as positioning and certain mobility.
From the above introduction, it is not difficult to see that eMTC and NB-IoT have their own advantages, and have certain coverage in terms of characteristics, and it is difficult to have very clear boundaries. For the relationship between the two, Qualcomm believes that the two technologies are complementary and each applies to different IoT usage scenarios. At the same time, LTE narrowband technology and existing 2G/GSM multimode coexist.
From the comparison of NB-IoT and eMTC technologies, look at the selection strategies of China's three major operators on NB-IoT and eMTC.
Third, application strategy analysis and recommendations
The development and application of new technologies cannot be determined only by their own technical characteristics, but also by the needs of users, policy support, and promotion of the industrial chain.
1. Business needs
The first type of business: water meters, electricity meters, gas meters, street lamps, manhole covers, garbage cans and other industries / scenarios, with static, small amount of data, low latency requirements, but for working hours, equipment costs, network coverage, etc. More stringent requirements. For such services, technically NB-IoT is more suitable.
From the comparison of NB-IoT and eMTC technologies, look at the selection strategies of China's three major operators on NB-IoT and eMTC.
The second type of business: elevators, smart wear, logistics tracking and other industries / scenarios, there are certain requirements for data volume, mobility, and delay. For this type of business, technical eMTC is even better.
It can be seen that different industries and application scenarios have different technical requirements. From the perspective of service demand, the three major operators should not exclude NB-IoT and eMTC.
2, alternative
For the first type of services, GSM/GPRS/EDGE can replace NB-IoT to some extent because of the mature development of the industry chain, low cost, and support for mobility and voice; however, due to coverage, power consumption, cell capacity, etc. It is impossible to completely replace it.
For the second type of service, CAT.0 is equivalent to eMTC because of its speed, mobility, voice, etc. It can also replace eMTC to a certain extent. The disadvantages are power consumption, coverage, etc. Further, CAT.1 and WCDMA/HSPA The eMTC technology can also be temporarily replaced to a lesser extent.
Therefore, if there is a complete GSM/GPRS/EDGE network, NB-IoT will not be so urgent; if there is an LTE CAT.0 network, eMTC may not have to be too anxious and necessary.
3. Characteristics of the three major operators' networks
China Unicom's 2G network (GSM) coverage is poor and has begun to retire; 3G network (WCDMA) has obvious advantages and can carry voice and medium- and low-speed data services; 4G network (TD-LTE/FDD LTE) is quite satisfactory, without CAT. 0/CAT.1 network.
China Telecom's 2G network (CDMA 1X) coverage is general; 3G network (EVDO) has obvious disadvantages and cannot carry voice; 4G network (TD-LTE/FDD LTE) has certain advantages, and CAT.1 and VoLTE are also coming soon. Web commercial.
China Mobile's 2G network (GSM) coverage is very complete, it can carry voice and very low-speed data services; 3G network (TD-SCDMA) has obvious disadvantages and cannot carry voice; 4G network (TD-LTE) also has certain disadvantages: no FDD license, There is no CAT.0/CAT.1 network.
In summary, China Unicom should have a strong demand for NB-IoT, and there is a certain demand for eMTC, but it is not strong; China Telecom has an urgent need for NB-IoT, eMTC is optional; China Mobile should be NB-IoT There are strong demands and there is also a certain demand for eMTC. which is:
NB-IoT: China Telecom>China Unicom>China Mobile
eMTC: China Mobile>China Unicom>China Telecom
4. Policy orientation
eMTC is a product of 3GPP's haste, the characteristics are not clear enough; NB-IoT is relatively more discussed and more targeted, Huawei is one of the technology leaders, and many Chinese companies participate, there is a certain discourse Rights and patent deployment.
Under this circumstance, combined with the current development situation, our government and industry organizations should give priority to the development of NB-IoT technology. eMTC will also support the technology and industry when the technology and industry are mature and the business needs are urgent.
5. Application strategy analysis and recommendations
From the comparison of NB-IoT and eMTC technologies, look at the selection strategies of China's three major operators on NB-IoT and eMTC.
Based on the above analysis, we believe and recommend:
China Unicom:
Before the 2G network is completed, it is necessary to develop and improve the NB-IoT technology as soon as possible;
eMTC can be used as a technical reserve. When foreign mature applications and domestic business needs are clear, they can be quickly launched through software upgrades. In 2018, commercial use of the entire network should not be necessary.
China Telecom:
Fully develop NB-IoT technology (and VoLTE);
In the case of the general promotion of CAT.1, eMTC can adopt a follow-up strategy to let Mobile and China Unicom go first.
China Mobile:
NB-IoT can adopt a synchronous follow-up strategy to maintain a certain degree of wait-and-see, so that Telecom and China Unicom can take a sneak peek, but not too much behind;
eMTC needs to be relatively more active. It can't be hung on a tree (NB-IoT). It can learn from the successful experience of foreign operators and promote it in China.
Type C Hub 8 In 1,Best Buy Usb C Hub,Usb C Hub For Macbook Pro,8 in 1 Type-C Multifunction Docking Station, 8 in 1 USB-C Multiport Docking Station
Shenzhen Konchang Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.konchang.com
