Modulation is to use the baseband signal to control the change of one or several parameters of the carrier signal, and the information load is formed on it to form the modulated signal transmission, and the demodulation is the inverse process of modulation, and the parameters of the modulated signal are obtained through a specific method. The change will restore the original baseband signal.
The purpose of modemThe purpose of modulation is to convert the analog or digital signal to be transmitted into a signal suitable for channel transmission. This means that the baseband signal (source) is converted to a band-pass signal of very high frequency relative to the baseband frequency. This signal is called a modulated signal, and the baseband signal is called a modulated signal. Modulation can be achieved by varying the amplitude, phase, or frequency of the carrier as the high frequency carrier changes with signal amplitude. The modulation process is used for the origination of the communication system. The receiving end needs to restore the modulated signal to the original signal to be transmitted, that is, the process of extracting the baseband signal from the carrier for the intended receiver (sink) processing and understanding. This process is called demodulation.
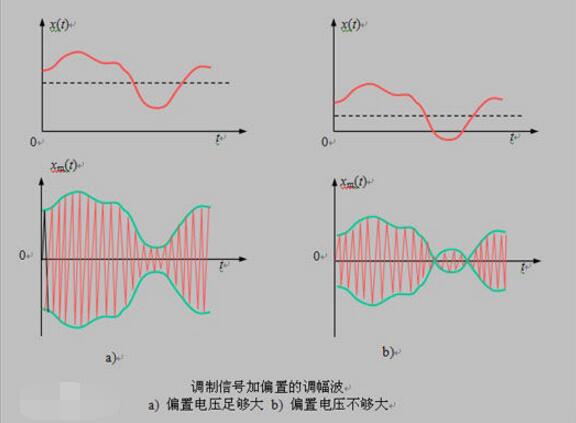
There are many types of modulation and the classification methods are also inconsistent. According to the form of the modulation signal can be divided into analog modulation and digital modulation. The modulation with analog signals is called analog modulation; the modulation with data or digital signals is called digital modulation. According to the type of signal being modulated can be divided into pulse modulation, sine wave modulation and intensity modulation (such as non-coherent light modulation). The modulated carriers are pulses, sine waves and light waves, respectively. Sine wave modulation has three basic modes of amplitude modulation, frequency modulation and phase modulation. The latter two are collectively called angle modulation. There are also some variants of modulation, such as single-sideband amplitude modulation and vestigial sideband amplitude modulation. Pulse modulation can also be classified in a similar way. There are also complex modulations and multiple modulations. Different modulation methods have different characteristics and performance.
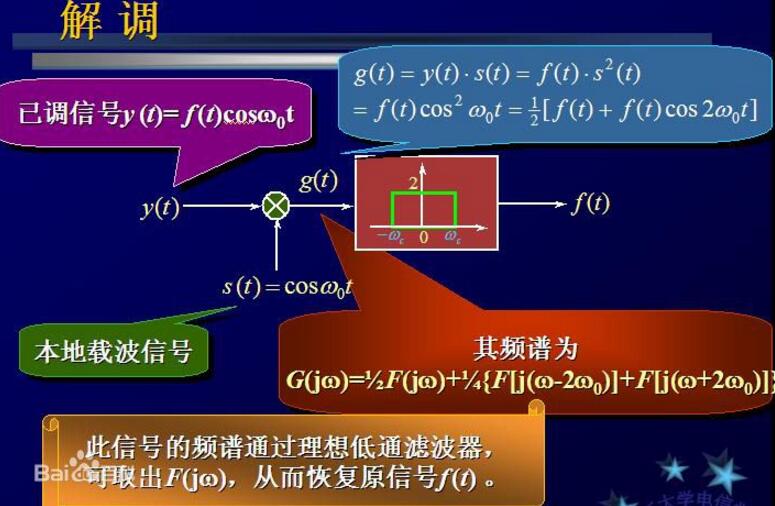
Demodulation is the process of recovering a message from a modulated signal carrying a message. In various information transmission or processing systems, the transmitting end modulates the carrier with the message to be transmitted, generating a signal carrying this message. The receiver must recover the transmitted message before it can be used. This is demodulation.
Demodulation is the inverse of modulation. Different modulation methods, demodulation methods are not the same. Corresponding to the modulation classification, demodulation can be divided into sine wave demodulation (sometimes also called continuous wave demodulation) and pulse wave demodulation. Sine wave demodulation can be further divided into amplitude demodulation, frequency demodulation and phase demodulation. Similarly, pulse wave demodulation can also be divided into pulse amplitude demodulation, pulse phase demodulation, pulse width demodulation and pulse code demodulation. For multiple modulation requires multiple demodulation.
Demodulation methods include sine wave amplitude demodulation, sine wave angle demodulation, and resonance demodulation techniques.
According to the modulation method can be divided into two categories: linear modulation and nonlinear modulation. Linear modulation includes AM, DSB-SC, SSB, and VSB. Non-linear amplitude modulation has strong anti-interference performance, including FM, FSK, PSK, and DPSK. The linear modulation feature does not change the original spectral structure of the signal, and the non-linear modulation changes the original spectral structure of the signal. According to the modulation, the modulation can be divided into continuous modulation and pulse modulation. According to the modulation technology, it can be divided into analog modulation technology and digital modulation technology. The main difference is that analog modulation is to continuously modulate certain parameters of the carrier signal, and the modulation parameters of the carrier signal are continuously evaluated at the receiving end, and the number Modulation uses some discrete states of the carrier signal to characterize the transmitted information. At the receiving end, only the discrete modulation parameters of the carrier signal are detected.
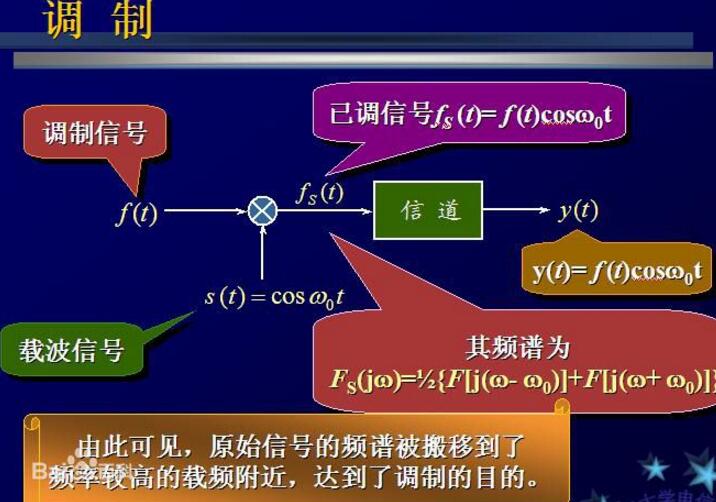
The modem is also called Modem, which is an essential hardware device for dialing into the Internet via telephone. Usually the computer uses a "digital signal" internally, and the signal transmitted over the telephone line is an "analog signal." The function of the modem is to convert the digital signal used internally by the computer into an analog signal that can be transmitted using the telephone line when the computer sends the information, and send it through the telephone line; when receiving the information, the analog signal uploaded from the telephone line is converted into a digital signal. Send it to the computer for it to receive and process.
Led Display,Led Screen,Led Display Screen,led monitor
Guangzhou Chengwen Photoelectric Technology co.,ltd , https://www.cwleddisplay.com
