The control theory of switching power supplies is a very abstract and sometimes daunting thing. System instability is a common problem, how to adjust? Why is there a problem with the system being mass-produced? There are many materials that talk about theory, and there are many mathematical theories that need to be understood.
A metaphor between a man and a woman, for your reference, as follows:
Let's talk about the pole first. A simple example is an RC filter. It is open circuit to DC C and short circuit to infinite high frequency C, so the amplitude of Bode plot is flat before the pole, and starts to decrease by -20dB/dec after the pole. The feeling of the pole is a man. Men usually start to be enthusiastic, but most of them can't stand the test of time. Whether it is for love or for the gradual loose hair, men are probably the same.
This zero is of course a woman. A simple example is the ESR zero of a capacitor. In DC, the resistance of the capacitor is infinite. As the frequency increases, the resistance decreases continuously. After the pole, the resistance of the remaining ESR resistor is no longer reduced. A man is a fire, a woman is a water, and a woman is not as strong as a man, but most of them have more endurance than a man. Women are also very impressed with love. It is not difficult to understand the difference between men and women by seeing Anna Karenina and his lover.
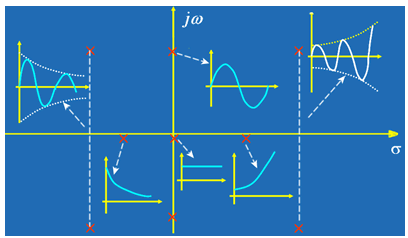
Zero point: When the input amplitude of the system is not zero and the input frequency makes the system output zero, the input frequency value is zero. Pole: When the input amplitude of the system is not zero and the input frequency makes the system output infinite (system stable destruction, oscillation occurs), this frequency value is the pole. Let's talk about the difference between the two.
First, the physical meaning of the zero and pole in the transfer function:
Zero point: When the input amplitude of the system is not zero and the input frequency makes the system output zero, the input frequency value is zero. Pole: When the input amplitude of the system is not zero and the input frequency makes the system output infinite (system stable destruction, oscillation occurs), this frequency value is the pole.
Second, at each pole, the gain is attenuated by -3db and phase shifted by -45 degrees. After every 10 times the pole, the gain drops by 20db. The zero point is opposite to the pole; at each zero point, the gain is increased by 3db and shifted by 45 degrees. After zero, the gain is increased by 20 db every ten times.
Closed loop gain A0: a / 1 + ab = 1 / b (when a is large), where a is the open loop gain and b is the feedback factor, which can be understood as the ratio of the feedback amount to the output, when the open loop gain approaches At infinity, the closed-loop gain is the reciprocal of the feedback factor.
Loop gain: T=a*b
3. For the op amp: the zero point of the transfer function of the closed-loop gain (1/b) is the pole of the loop gain (ab) transfer function; the pole of the transfer function of the closed-loop gain is the zero of the loop gain transfer function; In the feedback, it is hoped that the loop gain is greater than one before the phase drops to 180 degrees, so we need to eliminate the pole of a loop gain function (ie closed-loop gain zero) to avoid oscillation.
T Copper Tube Terminals,Non-Insulated Pin-Shaped Naked Terminal,Copper Cable Lugs Terminals,Insulated Fork Cable Spade Terminal
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lycopperlugs.com
