With the increasing enrichment of mobile Internet services and the rapid scale-up of various applications, the new mobile Internet business model has gradually matured, more and more mobile data service users, and mobile data service traffic has continued to grow, and also brought A lot of new problems, such as how to protect the experience of VIP customers, provide differentiated services; how to properly control the long-term occupation of wireless resources such as QQ and WeChat; how to effectively control the unlimited bandwidth users in monthly; streaming media, etc. How to protect high-value users and so on.
The value contribution of different business unit bits is very different. Nowadays, under the pressure of speed-up and fee reduction policy, the problems of increasing revenue and increasing revenue are becoming more and more prominent. How to distinguish the business and carry out real-time scientific control of the network resources occupied by users is reasonable for operators. It is especially important to allocate network resources to maximize your own revenue. PCC, Policy Control and Charging, can be used to effectively solve these problems.
Problems facing mobile data business operations
First, the incremental growth of mobile data services does not increase. From the perspective of the recent operation of mobile data services, the bell-curve effect between traffic growth and business revenue growth has become more and more obvious. This is mainly due to the rapid decline in the value of unit business caused by market competition, and the majority of the value of data services is caused by content or business application providers.
Secondly, there is a lack of differentiated service operation capability. In the existing operation, the network cannot provide differentiated services for users. The best-effort, first-come-first-served strategy is adopted in the entire operation to allocate network resources, resulting in some low network. Value-based services such as QQ, WeChat, etc., and users with unlimited monthly traffic are not occupied for a long time, and cannot guarantee the business resource requirements of high-value businesses and VIP customers.
Finally, the business distribution is uneven. Due to the mobility characteristics of mobile data services, there will be sudden growth in business in different regions such as university districts, central commercial districts, centralized residential areas, and commercial districts, resulting in these specific In the scenario, the service resources are insufficient, the quality of the user service application is degraded, or the service cannot be used. At the same time, these specific scenarios will also have a huge impact on the traditional voice service, which seriously affects the experience of the user's business application, greatly reducing the stickiness of the users on the network.
Principle of PCC technology
The PCC is mainly composed of a Policy and Charging Rule FuncTIon (PCRF), a SubscripTIon Profile Repository (SPR), a Policy and Charging Enforcement FuncTIon (PCEF), and an ApplicaTIon Function (ApplicaTIon Function). The composition is as shown in the figure below.
The PCRF is responsible for policy management, user management, and subscription management functions, and provides PCEF with differential charging, gating, end-to-end QoS guarantee, and shaping rate-limiting network control functions; SPR is responsible for storing all subscribers or subscription-related information. , including the service allowed by the subscriber, the priority of the service, the QoS information, etc.; the PCEF is upgraded by superimposing on the GGSN, and has the DPI function of the service depth identification capability, which is responsible for the detection of the service data flow, the policy execution, and the flow-based charging, etc. Features. The AF is located on the service platform and is responsible for communicating with the PCRF and interacting with dynamic sessions.
The service implementation process of the entire PCC control technology is as follows: the PCEF deep parsing service packet is reported to the PCRF through the Gx interface to perform the policy control rule matching, and the SPR is simultaneously coordinated. When the matching succeeds, the PCRF issues the control rule to the PCEF, and the PCEF can be executed during the execution. Through the GTP-U+BSSGP protocol transparent transmission mode, the end-to-end full-range control is completed; if the matching is unsuccessful, the message is unconditionally released, and the business process is the same as the original processing flow.
PCC technology features 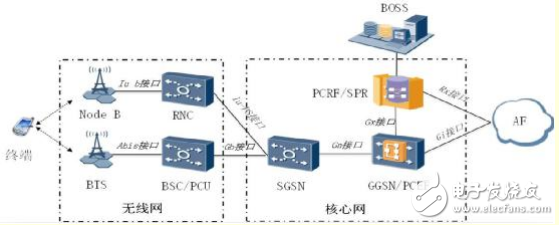
First, network resources can be optimized. Currently, mobile network resources of operators are established and spontaneous, resource utilization is low, and allocation is unreasonable. PCC can provide differentiated control based on services, optimize the allocation of small packet service resources, and make fair use of traffic in hotspot areas, which can maximize the application of network resources.
Optimize small packet business resource allocation. Instant messaging applications such as QQ and WeChat have small data packets and small traffic, but the number of users is large. The frequent transmission and reception of small packets will generate a large number of wireless resource allocation requests, greatly reducing the utilization efficiency of network data channels. Caused a big impact. After the PCC is introduced, the small data packet application is identified on the core network side, and the service identifier and the QoS policy are transmitted to the wireless side, and the wireless side identifies the service identifier and QoS, and implements a specific resource optimization strategy.
Enable fair use of traffic in hotspots. With the decline of traffic tariffs and the popularity of smart terminals, P2P and streaming video services have become new business growth points for mobile Internet. The number of such users is small, but the traffic of a single user is large, and the overall traffic is large. In particular, video services occupy a large amount of network resources, forming local congestion of wireless resources and affecting the experience of other users. Through the PCC implementation strategy formulation, in the busy hour busy area, the usage traffic is accumulated. When a certain threshold is exceeded, the bandwidth management is performed, the over-use behavior is controlled, and the resources are released to other users and services, which embodies the reasonable situation under the limited resources. The principle of fair distribution.
Secondly, it can provide differentiated services and effectively support market operations. PCC can interoperate with BOSS to build a bridge between market operations and networks, and extend market operations to the network level. With the help of PCC's differentiated control capabilities, the marketing department can customize differentiated network control strategies for different user service levels, tariff packages, and proprietary services.
Achieve user-level differentiation. According to market operation needs, operators generally classify users according to certain principles, but lack the ability to differentiate services for users. With the introduction of PCC, operators can define higher network priorities for high-end users and pass the priority from the core network to the wireless side through end-to-end QoS, so that users can get more when the network is idle or busy. A guaranteed service experience, while lower priority users can reduce their service access rate or limit their service access.
Achieve differentiation based on user packages. The traffic usage between the data service packages is very uneven. A small number of users consume most of the traffic, and some of the monthly unlimited traffic plan users have uncontrollable use of resources seriously affecting the service experience of other users. PCC-based differentiated policy control can limit low-value users and protect high-value users. For low-value users, they can accumulate their traffic usage. When a certain threshold is exceeded, they limit their service bandwidth during busy hours and limit their resources. abuse.
Recommendation and guarantee of self-operated business. The traditional packet network cannot provide differentiated control based on the operator's own business and other mobile Internet services, and does not make good use of the advantages of its own pipeline to give more resources to the self-operated business. After the operator introduces the PCC, it can control the user's service level when the user uses the self-operated service, and deliver the service level to the wireless side through end-to-end QoS to obtain a better service experience than the common Internet application. Enhance the competitiveness of self-operated business.
Typical application scenario analysis
Based on the application scenario of the service-based control policy, such control mainly obtains an exact match of the service type field after deeply parsing the message. Such a control strategy only needs to preset important parameters such as the priority of the service and the service threshold in the PCRF to achieve priority resource allocation for high-value or key services; on the other hand, it can also perform video and P2P download services. Effective control.
Based on the user priority control policy application scenario, such control mainly obtains the exact match between the user IMSI and the MSISDN number segment after deeply parsing the message. This type of control policy needs to match the user subscription database in the SPR first. After the SPR is matched, the priority parameter of the user is obtained. The ARP and the name of the control rule preset in the triggering PCRF trigger the control policy in the PCRF so that the high-end user can When congestion occurs, it can occupy more network resources preferentially; it also provides effective control means for users with high risk of arrears. In order to prevent the control policy from enabling the low-priority users to use the service, only the proportion of the resource occupation is set in the control rule, and the absolute access rate threshold is not set.
Based on the time-based control strategy application scenario, the operator can set different policies, including different QoS policies and charging policies, to achieve network optimization purposes according to the user's usage habits and the busy and idle conditions of the network. . For example, 20:00-22:00 is the peak period of network traffic. The use of a large number of video and P2P download services affects the normal use of other data services and even voice services. Operators can reduce video and P2P downloads during this time period. The bandwidth of the service prevents the network from being congested, and also maximizes the utilization of network resources, thereby increasing the revenue of the operator.
In the actual PCC technology application scenario, there is generally no coexistence of multiple problems. Only a single control strategy needs to be deployed to alleviate the problems in data service operations, but in some university districts, central business districts, and concentrated residential areas in the city. In a special scenario such as a business district, multiple problems coexist. It is necessary to analyze the characteristics of users, business use, and major operational problems. For different dimensions, scientifically and effectively combine the control strategies of PCC technology in various typical scenarios.
Hongkong Onice Limited , https://www.ousibangvape.com
