Robots are not only the basic equipment of high-end manufacturing, but also the living service facilities of human society. With the development of artificial intelligence and other technologies, robots are spreading from industrial applications to life service applications. At the time of industrial transformation, it is the window of opportunity for latecomers. .
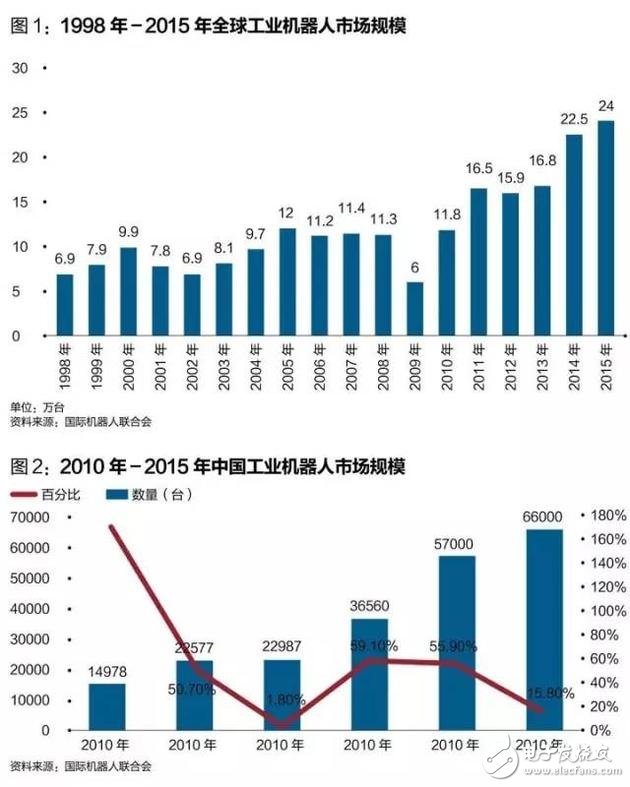
In 2010, China became the world's largest manufacturing power. In 2013, China became the largest market for industrial robots in the world. In 2015, the Chinese market sold a total of 66,000 industrial robots, ranking first in the global market for three consecutive years.
The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) predicts that China's industrial robot sales will reach 150,000 units in 2018, accounting for more than one-third of global sales, and nearly four times the size of Japan's second largest market (40,000 units). The China Robotics Industry Alliance predicts that the total size of China's industrial robot market will reach 600 billion yuan in the next decade.
Before 2012, the Chinese industrial robot market was dominated by foreign brands. Later, under the dual stimulation of policies and markets, domestic brands broke out, and by 2015, they already accounted for 32.5% of the domestic market.
In May 2015, the State Council issued the "Made in China 2025 Action Plan", and high-end CNC machine tools and robots were listed as one of the ten key points. In April 2016, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the National Development and Reform Commission, and the Ministry of Finance jointly issued the "Robot Industry Development Plan (2016-2020)", proposing that "by 2020, the annual production of self-owned brand industrial robots will reach 100,000 units."
Not only the central government, but also local governments at all levels have also focused on the robotics industry. Put forward the industrial development goals, and give support policies from financial subsidies to land use and project establishment.
Under the time and place, can Chinese robot companies seize the opportunity to rise to the next level?
At present, China's industrial robot application market is rapidly expanding from the automotive industry to the general industry, which means that emerging companies can avoid the advantages of giant companies in the automotive industry and gain their own place in emerging markets.
With the combination of artificial intelligence technology and the new generation of information technology and robots represented by Internet of Things, big data, and cloud computing, the robot industry is entering a period of technological explosion. The future of robots will become more and more intelligent, and the scope of application will be extended to service areas outside the industry, which will bring more imagination to the robot industry. And those companies with unique technology will undoubtedly stand at the top of the wave.
According to the statistics of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, there are more than 800 robot companies in China. According to the plan of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, by 2020, China should form a relatively complete industrial robot industry system, cultivate more than three leading internationally competitive enterprises, and build more than five supporting industrial clusters, with a product share of 50 in the high-end market. %the above.
Who can stand out and become a leading company? The majority of industry contacts in Caijing believe that, combined with market performance and innovation potential, Xinsong Robot Automation Co., Ltd. (300024.SZ), Guangzhou CNC Equipment Co., Ltd., Anhui Eft Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd., Nanjing Eston Automation Co., Ltd. Companies such as Shanghai Xinshida Robot Co., Ltd. (002527.SZ) are strong candidates. But at the same time, as competition intensifies, hundreds of robotics companies will be eliminated.
Chinese market broke out
The market scale is already the largest in the world and is still growing at a high speed. The market structure is expanding from the general manufacturing application of the automotive industry, which is mainly a fast vector.
The growth of the Chinese industrial robot market is related to the automotive industry. Whether in the world or in China, the automotive industry has always been the largest application market for industrial robots. In the 1970s, Kawasaki Heavy Industries of Japan introduced industrial robot technology from the United States and industrialized it, first applying it to its own motorcycle production line, and later popularizing it in the automotive industry.
China's industrial robot market began to accelerate after 2008, and it ushered in the first explosive growth in 2010. In the year, the Chinese market sold 14,978 industrial robots, with sales increasing by 171% year-on-year.
The growth of China's industrial robots this year was mainly due to the increase in investment in the automotive industry. In 2009, China's auto sales jumped to the top in the world, and the policy encouraged the increase of market concentration. From 2009 to 2010, Chinese joint venture brands and self-owned brand automakers expanded their auto production capacity on a large scale.
According to IFR data, in the industrial robot application market in 2010, the proportion of robots used for welding, painting and various assembly operations is about 55%, which is mainly used in the automotive industry. From the perspective of growth rate, the fastest growth is the arc welding robot used in the manufacturing process of automobile manufacturing, which increased by 186% year-on-year, accounting for 39% of the total installed capacity of industrial robots that year.
Another growth driver for the Chinese industrial robot market comes from the upgrading of general industry demand and replaces the increasing cost of labor.
According to the "2016 First-line Employment Management Research Report" released by China Human Capital Research and Data Service Center, the average annual income of ordinary first-line employees of manufacturing enterprises in first- and second-tier cities in 2015 was about 58,000 yuan. This income level has increased by about six times compared to the average manufacturing wage in 2000. At the same time, in 2009, in the manufacturing-intensive areas such as the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta, the phenomenon of “labor shortage†began to appear on a large scale.
China's current industrial transformation is similar to Japan's scenario in the 1970s and 1980s. At that time, Japan's industrial structure shifted from heavy chemical industry to capital and technology-intensive industries such as semiconductors and automobiles. This led to a decrease in the proportion of manufacturing in GDP, but the demand for industrial robots continued to grow.
In 2008, Guangdong, China's largest economic province, took the lead in promoting industrial transformation, transferring and restricting labor-intensive enterprises, and promoting the transformation of industries into advanced manufacturing and strategic emerging industries. By 2012, the trend of industrial transformation has spread to Zhejiang and other places. In 2015, the State Council issued the "Made in China 2025", and the transformation and upgrading of China's manufacturing industry became a national policy.
Reflected in the industrial robot application market, it is the rapid growth of demand in the general industrial market. According to data from the China Robotics Industry Alliance, in 2013, the Chinese market sold about 37,000 industrial robots, making it the world's largest industrial robot market. In 2015, China sold about 66,000 industrial robots, accounting for more than a quarter of the global industrial robot market.
From the perspective of the application industry, the Chinese industrial robot market is rapidly expanding from the automotive industry to the general industry. In 2015, the proportion of the automotive industry in the industrial robot market has dropped to 36.8%, and industrial robot applications have expanded to more industries. From the application field, the highest sales ratio in 2015 was handling and loading and unloading robots, accounting for 43.8% of the total sales. Such robots can be widely used in general industries of various categories.
China's industrial robots still have huge room for growth. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, in the year of 2015, the number of industrial robots used per 10,000 workers in China's manufacturing industry was 36, while the global average level was 66. 200 units. The density of robots in Japan, Korea, and Germany is more than 10 times that of China.
In December 2013, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology formulated the "Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Development of the Industrial Robot Industry", and for the first time proposed the goal of "the robot density (the number of robots used per 10,000 employees) reached 100 or more by 2020."
In April 2016, Vice Minister of the Ministry of Industry and Information, Huai Jinpeng, said at the 4th China Electronic Information Expo that the annual sales volume of China's industrial robots will reach 150,000 units in 2020, and the output value of China's robot industry will exceed 100 billion yuan. The annual output of robots will reach 260,000 units.
Road Stake Actuator,Used Linear Actuators,Linear Screw Actuator,Electric Lift Mechanism
Kunshan Zeitech Mechanical & Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.zheteswitches.com
